TOOLS
IC maps paint a picture of standards in action
By Machel Mills-Miles
Categories: Fundamentals, Implementation, Leadership, Standards for Professional Learning, System leadershipJune 2022
Translating the vision of Standards for Professional Learning into daily practice can be challenging. To guide educators through the process, Learning Forward has created Innovation Configuration (IC) maps to show what it looks like for stakeholders to implement the standards within their specific roles and responsibilities.
IC maps are valuable tools that describe the major components that need to be in place for an innovation to succeed, acknowledging that individual stakeholders adapt new practices as they implement them and grow into full implementation (Hall & Hord, 2010; Hord et al., 2006). Innovation Configurations were born out of the recognition that stakeholders typically implement innovations in a variety of ways and stages of development, so the maps show a progression of specific behaviors from the early stages of implementation to ideal implementation.
The IC maps for Standards for Professional Learning bring detail and specificity to the concepts presented in the standards and describe actions for educators in roles such as system/central office leaders, principals, coaches, and external providers. They are not intended to prescribe every move educators should make to ensure high-quality professional learning; rather, they present high-leverage actions and behaviors that are most likely to lead to improved outcomes.
IC maps can be used to guide the planning, implementation, monitoring, and evaluation of professional learning. When used collaboratively, they foster dialogue around best practices and provide direction for growth related to professional learning.
We encourage you to familiarize yourself with the IC maps through the sample we have included here, which goes into depth about how central office leaders can address the Implementation standard. Then we invite you to explore the interactive IC maps specific to your role on our website by going to standards.lfstage.xyz and clicking on “Action Guides.” You’ll see the Action Guides for several roles, and IC maps included with the guides for system/central office leaders, principals, coaches, and external providers.
Once you’ve selected the role you want to explore, take the following steps:
Select the “IC maps: Levels of implementation” button.
Next, select one of the 11 standards.
Continue by choosing one of the three constructs for that standard. Each standard covers three key constructs or concepts in depth; for the IC maps, those concepts serve as a means of breaking down the standard into further detail to allow educators to investigate specific actions.
Then, select a desired outcome for that construct. The desired outcome is an observable impact.
Finally, you’ll see a table with the levels of implementation listed for that outcome. The levels progress from ideal to entry, and therefore outline a possible path of progress over time. Note that some outcomes have more levels of implementation than others.
IC maps have been a powerful tool for implementing Standards for Professional Learning for many years. As you delve into the newly revised standards, we look forward to hearing from you about how they are informing your work and making a difference for your educators and students.
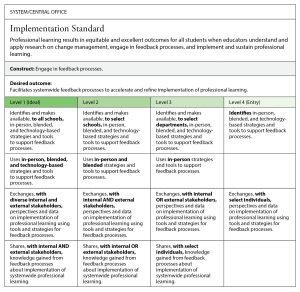
Example of an IC Map for the implementation standard
This Innovation Configuration map below presents descriptions of behaviors that central office leaders and staff can take to implement one concept, or construct, of the Implementation standard: engaging in feedback processes.
This IC map zooms in one of the three desired outcomes for that construct: facilitating systemwide feedback processes to accelerate and refine implementation of professional learning. The rows of the table represent specific behaviors or actions educators should take to meet that desired outcome.
For each behavior (row), the IC map details four levels of action. The columns represent those four levels. In contrast to many progressions, the highest degree of impact is level 1 (ideal implementation) and is listed at the left of the progression. The degree of impact descends to level 4 (entry-level implementation) from left to right.
To see a larger image of the IC Map, download the pdf at the bottom of this page.
Download pdf here.
Ways to use IC Maps
There are many ways to use this and other IC maps, including:
- Conduct an informal self-assessment of your progress, individually or with a team, in addressing the standard by circling your current level of action;
- Choose one or more IC maps and engage in reflective journaling about your short- and long-term goals and progress toward meeting them;
- Facilitate a discussion with your team about your current implementation of the standards and your goals; and
- Show your colleagues and leaders what it means to implement the standards and how taking the specific actions listed will help move your system toward strategic goals and, ultimately, higher-quality teaching and learning.
References
Hall, G. & Hord, S. (2010). Implementing change: Patterns, principles, and potholes (3rd ed.). Prentice Hall.
Hord, S., Rutherford, W., Huling-Austin, L., & Hall, G. (2006). Taking charge of change. SEDL.
Categories: Fundamentals, Implementation, Leadership, Standards for Professional Learning, System leadership
Recent Issues
LEARNING TO PIVOT
August 2024
Sometimes new information and situations call for major change. This issue...
GLOBAL PERSPECTIVES
June 2024
What does professional learning look like around the world? This issue...
WHERE TECHNOLOGY CAN TAKE US
April 2024
Technology is both a topic and a tool for professional learning. This...
EVALUATING PROFESSIONAL LEARNING
February 2024
How do you know your professional learning is working? This issue digs...










